Digital Transmission Content Protection ("DTCP") technology protects high-value digital motion pictures, television programs and audio against unauthorized interception and copying in the home and personal environment (e.g., between a digital set top box and digital video recorder, or between a personal computer and a digital TV).
How does DTCP work?
A device enabled with DTCP determines whether it is connected to other devices that implement the DTCP protection technology. Content encoded for DTCP protection is encrypted and securely transmitted only to recording and display devices that implement DTCP. The content carries information indicating whether and to what extent the content may be copied.
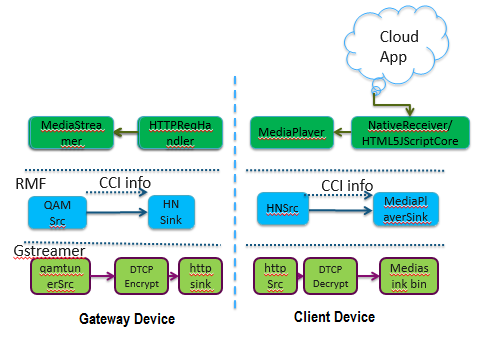
Filter elements for content encryption and decryption
There are two gstreamer filter elements are used for content encryption/decryption.
DTCP Protection
All DTCP encryption and decryption uses common set of provided gstreamer elements, The gstreamer elements uses DTCP manager API. Each SoC provides binary DTCP encryption/decryption library to support the DTCP Manager API.
How to enable/disable DTCP?
At first, user need to verify that the current build of the box supports to enable/disable DTCP.
If it's yes, following the next steps

DTCP encryption and decryption are used for protecting contents over network.