This page is under development |
Figure 1 - Architectural view of PSM sub-system
Figure 2 - Initialization of PSM sub-system
Configuration files are saved as below on the device:
/fss/gw/usr/ccsp/config/bbhm_def_cfg.xml
/nvram/bbhm_bak_cfg.xml
/nvram/bbhm_cur_cfg.xml
Factory reset removes the configuration files from nvram and copies default file to nvram.
To prevent system configuration file from becoming corrupted or lost when the device is suddenly rebooted or power loss conditions, following counter-measures are in place:
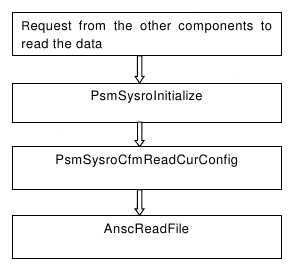
Figure 3 - Reading Configuration
PsmSysroCfmReadCurConfig/PsmSysroCfmReadDefConfig - This function is called to read the current or default Psm configuration into the memory. AnscReadFile - performs a sequential read
Restore configuration is tried first from the current system file. If it passes the verification, read is done otherwise restore configuration is tried from the backup system file. If it passes the verification, read is done otherwise restores the factory default configuration. This step has to succeed since there is no any other plan to back it up.
Figure 4 - Retrieving Parameter
Using CLI utility:
psmcli get <parameter name as in bbhm file>
Eg: psmcli get eRT.com.cisco.spvtg.ccsp.Device.WiFi.NotifyWiFiChanges
Figure 5 - Setting Parameter
Using CLI utility:
psmcli set <parameter name as in bbhm file>
Eg: psmcli set eRT.com.cisco.spvtg.ccsp.Device.WiFi.NotifyWiFiChanges true
Syscfg_create.exe executable creates shared memory with user configuration data (/nvram/syscfg.db). This is present in the code base at the location /ccsp/utopia/source/syscfg

Apply_system_defaults.exe executable reads the data from system_defaults file (path: /etc/utopia/system_defaults) and compares with syscfg.db, in case of any data is missing in syscfg, those defaults are written in to shared memory. On start of any module, data is read from the shared memory during initialization.
If syscgf.db does not exists (e.g in case of factory reset) apply_system_defaults.exe writes all default data on to shared memory and syscfg_commit() gets called which in turn creates syscgf.db.
Gw_prov_utopia exe calls Init script. Init script executes all executables present in /etc/utopia/registration.d/ directory. 10_firewall exe is responsible for firewall events and it registers for sysevent callback with service name as firewall. Handler script is firewall_log_handle.sh. If any firewall event occurs sysevent is triggered with firewall-restart event name.
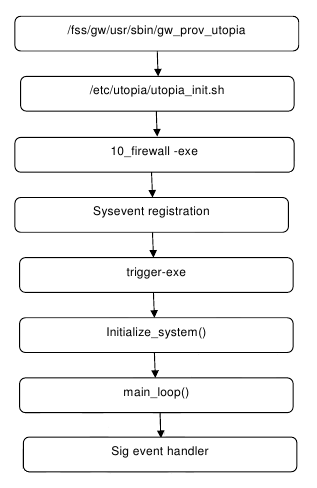
Firewall Initialization Process

On firewall-restart event service_start() method gets called. Ip4table and Ip6table rules are prepared by reading data from shared memory, written into /tmp/.ipt and /tmp/.ipt_v6 files respectively. Iptable rules are restored using these files.
Following sequence explains flow when a SET from SNMP, TR69 or CLI is done:
Eg. Second row entry details are saved as shown below in xml.
pcms_2::method=URL
pcms_2::always=1
pcms_2::end_time=
ManagedSiteBlock_2=pcms_2
pcms_2::alias=cpe-BlockedURL-2
pcms_2::days=
pcms_2::site=https://www.wellsfargo.com
pcms_2::ins_num=2
pcms_2::start_time=
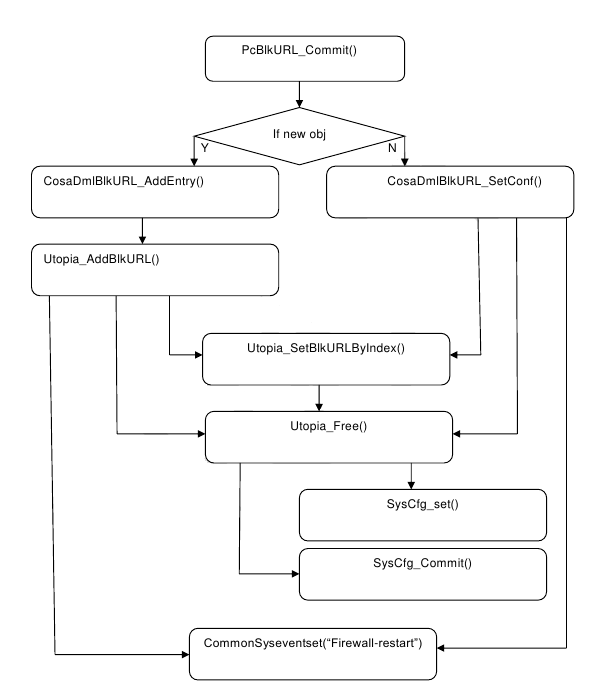
Example set flow for PC URL