 |
RDK Documentation (Open Sourced RDK Components)
|
 |
RDK Documentation (Open Sourced RDK Components)
|
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| ACS | Auto-Configuration Server |
| CPE | Customer Premises Equipment |
| CWMP | CPE WAN Management Protocol |
| NAT | Network Address Translation |
| STUN | Simple Traversal of UDP through NATs |
| B-NT | Broadband-Network Termination |
| DT Schema | Device Type Schema |
| RPC | Remote Procedure Call |
| DT Instance | Device Type Schema instance document |
| ACL | Access control list |
| ADSL | Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line |
| AES | Advanced Encryption Standard |
| ASCII | American Standard Code for Information Interchange |
| ATA | Analog terminal adapter |
| ATM | Asynchronous Transfer Mode |
| BOOTP | Boot Strap Protocol |
| CGI | Common Gateway Interface |
| CN | Common Name |
| CSRF | Cross-site request forgery |
| DHCP | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol |
| DNS | Domain Name System |
| DSL | Digital Subscriber Line |

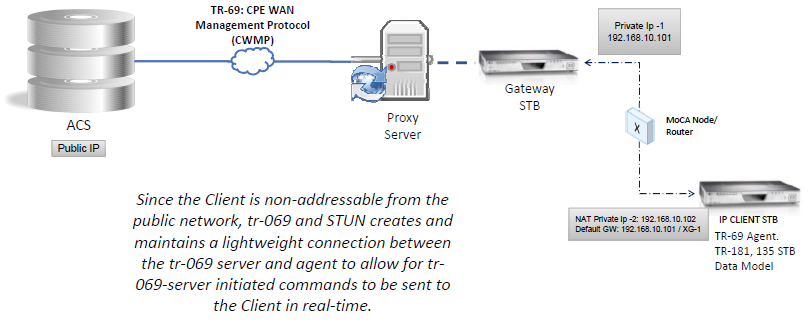
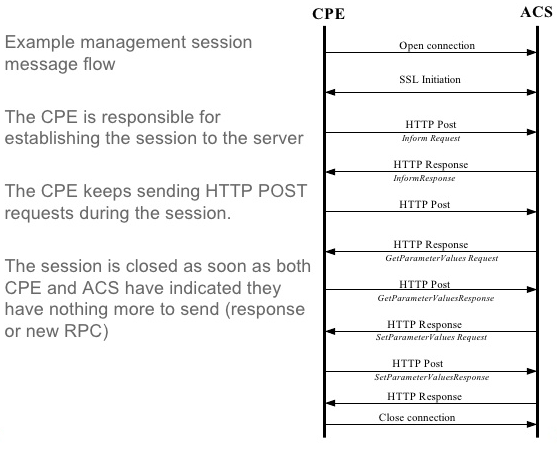
Modules | |
| TR-069 Device Management | |
| TR-069 Diagnostics | |
| When the diagnostic initiated by the ACS is completed successfully or not, the CPE MUST establish a new connection to the ACS to allow the ACS to view the results, indicating the Event code "8 DIAGNOSTICS COMPLETE" in the Inform message. After the diagnostic is complete, the value of all result parameters MUST be retained by the CPE until either this diagnostic runs again, or the CPE reboots. After a reboot, if the CPE has not retained the resultant parameters from the most recent test, it MUST set the value of this parameter to None. Modifying any of the writable parameters in this object except for this one MUST result in the value of this parameter being set to None. While the test is in progress, modifying any of the writable parameters in this object except for this one MUST result in the test being terminated and the value of this parameter being set to None. While the test is in progress, setting this parameter to Requested MUST result in the test being terminated and then restarted using the current values of the test parameters. | |
| TR-069 Firmware Download | |
| TR-069 Gathering Periodic Information | |
| TR-069 Host Interface | |