WIP
Scope:
This guide will help RDK-B community to port OneWifi on their platforms
Target Audience:
RDK-B Software Architects and Engineers
Prerequisites:
TBD
Supported platforms:
- Raspberry Pi4 64 bit
- Raspberry Pi4 32 bit
Supported yocto version:
- Dunfell
- Kirkstone(supported from rdkb2023q4 official release)
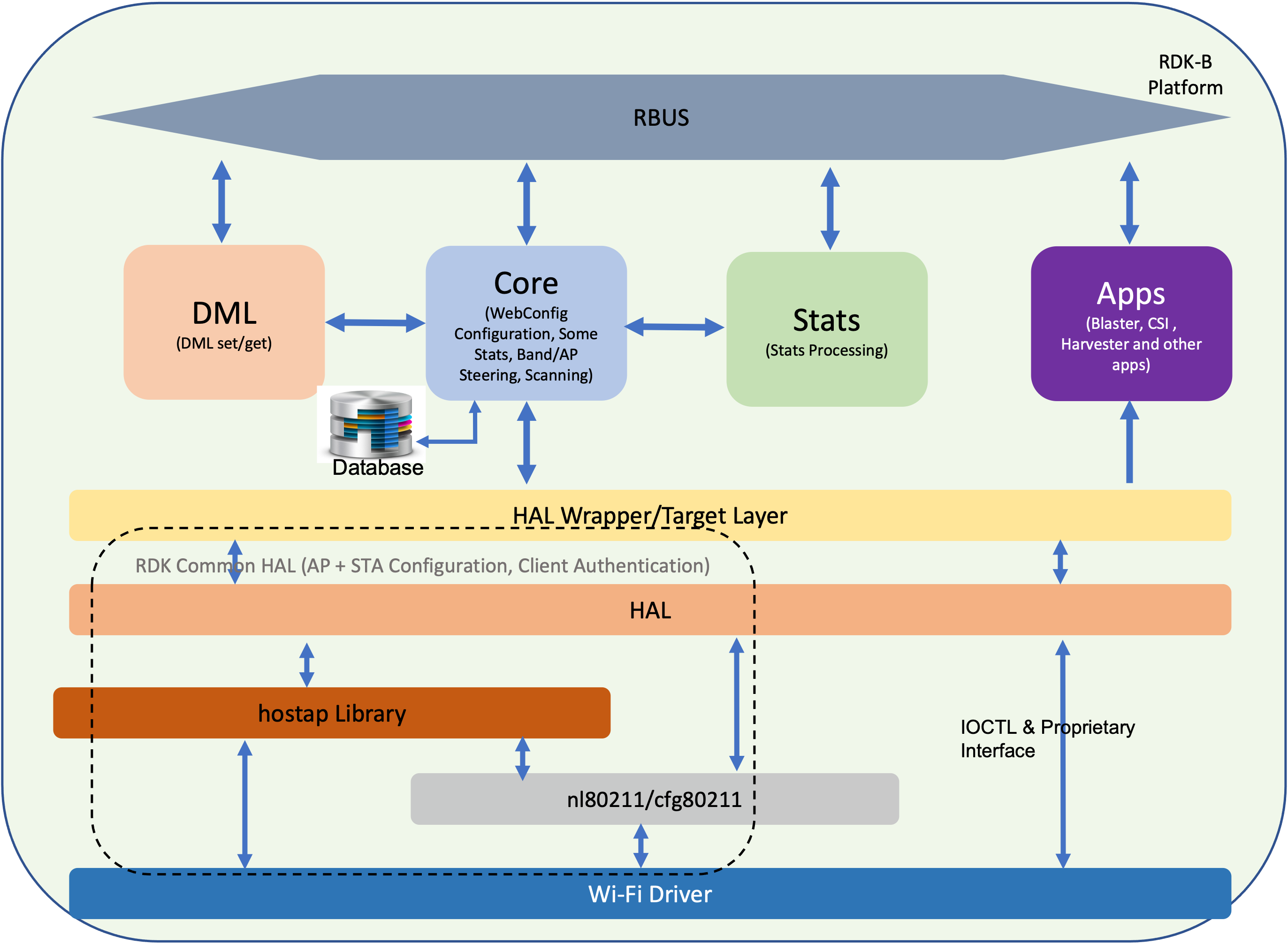
High level architecture:
The internal functional entities of the OneWifi process are as shown in the above diagram. OneWifi software architecture is essentially a multi-threaded software architecture, the three main threads are
- Core thread: this thread is the fundamental engine of the process that is responsible for all configuration of WiFi parameters, command/control/status response and WiFi state indications. The core thread is also responsible for steering related activities.
- DML thread: this thread handles the TR-181 set/get handlers.
- Apps thread: this thread is responsible for supporting all WiFi related application/features such as harvester, motion sensing, blaster, single client measurements etc.
The software architecture of working of each thread is detailed below.
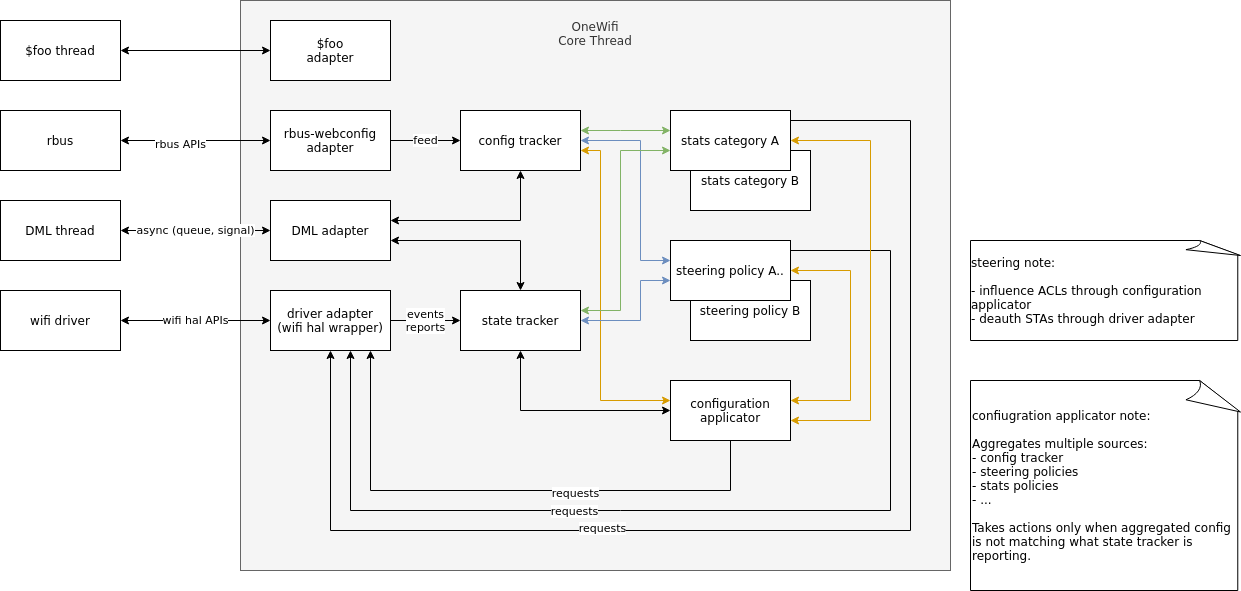
OneWiFi Thread Management, Inter Thread Communication and Data Handling
The diagram below depicts thread management and inter thread communication and data transfer in OneWifi. Threads essentially wait for condition and timeouts. If data needs to be processed, the data is posted into queue and the thread is signaled. The thread retrieves the data from the queue and processes the data
Core Functional Blocks/Subsystem
The core thread waits for events or messages, if there are events or messages in the FIFO queue, the thread retrieves the events or messages one after another and takes appropriate action. Three kinds of messages or events can be enqueued in the Core thread queue
- South bound messages received from WebConfig Agent or Ovsdb Managervia RBUS callback.
- South bound messages received from DML thread because of TR-181 set handler invocation
- North bound asynchronous Wi-Fi events from HAL or driver isuch as
- Client associations/disassociations
- VAP or interface Up/Down
- Registered 802.11mgmt frame reception
- Band Steering events
All south bound messages are decoded, parsed and validated by core thread. In case, the messages are successfully validated, the core thread uses Wi-Fi HAL function to configure Wi-Fi driver or baseband accordingly. if successful, core thread is also resonsible for updating the persistent database so that in case of reboot or power failure, the Wi-Fi subsystem of the CPE device maintain previous operating configuration. Core thread also handles Wi-Fi or Factory reset commands that may be triggered by messages enqueued by DML thread or during initialization sequence.
All north bound events are translated to state update in ovddb state tables using WebConfig encoded messages sent by core to ovsdb manager.
Core Thread Software Architecture
Some of the components described are as follows:
- Config Tracker - serves as an internal database for all Radio and VAP attributes. To be consumed by OneWifi internals, eg. stats policies, steering policies, configuration applicator, etc. Intended to be acting as a south bound interface and called by adapters to integrate them into specific systems, eg. rbus+webconfig.
- State Tracker - serves as a layer to shield OneWifi business logic modules from HAL API which is intended to not be fully object oriented.and to simplify its implementation, eg. event buffer overrun recovery handling, event order sanitization (sometimes implementations source events from multiple streams and their processing ordering is undefined).
- Configuration Applicator - uses inputs: Config Tracker and other mutators (coming from, eg. Stats or Steering policies) to generate configuration command(s) and submit them only if the assembled configuration command is out-of-sync with what State Tracker is reporting. Configuration Applicator is triggered for recompute by either Config Tracker, State Tracker or any of the registered mutators.
- Steering/Stats/Other policies - multiple entities implementing specific actions. Mostly interact with State Tracker, Configuration Applicator (as mutators), HAL wrapper (to perform world-visible actions) or between each other modules (Steering modules using some Stats).
- Rbus-webconfig adapter - adaptation logic which feeds Config Tracker based on Webconfig blobs. Essentially a translator to abstract Webconfig away from core logic. Foo thread / foo adapter - approach recommended on integrating other existing, or thread-heavy tasks. The OneWifi core is a single thread expecting no other threads interacting directly with its data structures or control flows, so adapters and their dispatch handlers are expected to be the entry/exit points between threads to simplify locking.
- HAL wrapper - virtually a HAL API that allows multiple backing implementations: Wifi HAL, Target API or other in the future. Intended to be mostly stateless and simple "pass through" - allowing out-of-order event delivery, etc. This allows simpler implementation for vendors. The task of sanitizing is handed to State Tracker for actual business logic consumers. The HAL wrapper API is highly aggregated (big blob call for configuration, singular calls for adequate actions like WPS PBC) with hints on which attributes are out-of-sync allowing implementations to optimize if desired. The wrapper is also capable of supporting multiple backing implementations at the same time (without requiring business logic implementation to be aware of any of that) to accommodate mixed vendor chips (on non-Wifi-Hal platforms) such as Broadcom + Quantenna.
All components are intended to schedule most of the actual work through separate dispatch handlers per object entities. This allows easy batching (to debounce and reduce ping-pong), time occupancy (to provide insight into possible stalls, or aid scheduling), forces idempotency (avoids some ab/ba logic issues, provides failure recovery procedures without additional explicit logic) and makes sure memory resource allocation is bound.
Operational Modes
OneWifi can operate in two modes, router and extender.
Router Mode
In router mode, the stack broadcasts front haul virtual access points that client devices may connect with. Total of seven such virtual access points are created on each radio and provide different kinds of services.
Extender Mode
TBD
Flow Diagram/Pseudo Code
Core Thread Pseudo Code
Message Sequence Diagrams
Initialization
Client Authentication
Epic details:
- REFPLTB-2020 - Getting issue details... STATUS
Approach followed:
- Full Management frame approach(Highly recommended for SoC vendors,OEM's and Operators)
- Event based approach(Only for Raspberry Pi4,Since there is no much support for full management from broadcom driver side we opted this approach.To continue using this approach,this should be discussed with Operators and RDK-B Architecture Review Board)
Step by step procedure:
Include rdkb2023q2 release on top of SoC SDK.this is the recommended rdkb stable release for OneWifi (rdkb-2023q2-dunfell)
Integration segments:
Dependencies to build OneWifi
Systemd Service file:
- onewifi.service
Create platform layer for mediatek platform,please consider raspberry pi as reference
- https://code.rdkcentral.com/r/plugins/gitiles/rdkb/components/opensource/ccsp/hal/rdk-wifi-hal/+/refs/heads/rdk-next/platform/
- https://code.rdkcentral.com/r/c/rdk/components/generic/rdk-oe/meta-cmf-raspberrypi/+/85744/1/meta-rdk-broadband/recipes-ccsp/hal/files/0002_onewifi_process_bringup_changes.patch
Manifest entries:
- Onewifi component entry in manifest file (OneWifi) and rdk-wifi-hal component entry in manifest (rdk-wifi-hal)
Layers to consider:
1.meta-raspberrypi ( Or )meta-cmf-soc-<soc name> ------- Firmware/drivers/kernel to be available
- For proposing a new component,please create a bb file here
2.meta-cmf-raspberrypi (Or) meta-cmf-<platformname> --------- RDK-B changes to specific to SOC platform
- All changes that need to be done for the primary recipe are handled in the form of bbappend
- Patches: Patches are recommended if the changes are very specific and tied with SOC platform code.
3.meta-cmf-broadband ----------- RDK-B changes which are common for all RDK-B community members
- All changes that need to be done for the primary recipe are handled in the form of bbappend
- Patches: Patches are recommended if the changes are very specific and tied with SOC platform code.
- All existing reference patches in Raspberry pi may not be applicable for real targets,Because of hardware limitation & functionality limitation we have added patches.
Bug fixing or feature enhancement:
- Bug fixing or feature enhancement done as part of OneWifi which are generic enough should come to OneWifi generic repo
Flags defined in Onewifi:
- Raspberry Pi has certain limitations on the driver side to support end to end use case of OneWifi and Build dependencies which are specific to comcast.to avoid such issues we have introduced a flag (_PLATFORM_RASPBERRYPI_) to keep it under conditional compilation.for Real targets we dont really need this flags
Bulk atomic HAL apis for common configuration
| wifi_hal_sendDataFrame |
| wifi_hal_newApAssociatedDevice_callback_register |
| wifi_hal_apDeAuthEvent_callback_register |
| wifi_hal_apDisassociatedDevice_callback_register |
| wifi_hal_register_frame_hook |
| wifi_hal_disassoc |
| wifi_hal_send_mgmt_frame_response |
| wifi_hal_init |
| wifi_hal_getHalCapability |
| wifi_hal_setRadioOperatingParameters |
| wifi_hal_createVAP |
| wifi_hal_startScan |
| wifi_hal_connect |
| wifi_hal_get_default_country_code |
| wifi_hal_get_default_ssid |
| wifi_hal_get_default_keypassphrase |
| wifi_hal_get_default_wps_pin |
| wifi_hal_get_default_ssid |
| wifi_hal_get_default_radius_key |
| wifi_hal_setRadioOperatingParameters |
| wifi_hal_staConnectionStatus_callback_register |
| wifi_hal_scanResults_callback_register |
| wifi_hal_mgmt_frame_callbacks_register |
| wifi_hal_getRadioVapInfoMap |
| wifi_hal_delApAclDevice |
| wifi_hal_addApAclDevice |
| wifi_hal_kickAssociatedDevice |
| wifi_hal_setApWpsButtonPush |
| wifi_hal_setApWpsPin |
| wifi_hal_disconnect |
| wifi_hal_getRadioOperatingParameters |
| wifi_hal_getScanResults |
Stats implementation:
- This is vendor specific.we can use vendor based implementation from device specific HAL.pls refer this ticket for reference( REFPLTB-2510 - Getting issue details... STATUS )
wifi database:
rdkb-wifi.db
64 bit build support:
- Comcast doesnt have 64 bit support in the current platforms.from RDK team side we have Raspberrypi 4 platform which support 64bit.we have supported Onewifi as part of this platform and fixed lot of alignment issues and warning treated as errors
Difference Between CcspWifiAgent and OneWiFi Apply settings
CcspWifiAgent:
dmcli eRT setv Device.WiFi.Radio.2.X_CISCO_COM_ApplySetting bool true dmcli eRT setv Device.WiFi.Radio.1.X_CISCO_COM_ApplySetting bool true
Onewifi
#Any dmcli commands specific to SSID and AccessPoint execute the Below Access Point Related apply settings dmcli eRT setv Device.WiFi.ApplyAccessPointSettings bool true #Any dmcli executions specific to Radio level use the below Radio apply settings command dmcli eRT setv Device.WiFi.ApplyRadioSettings bool true
Debugging tips:
Below are the list of logs present in /rdklogs/logs for Debugging OneWiFi Issues.
For Additional in-depth Debugging one should enable below commands ,
- touch /nvram/wifiMgrDbg
- touch /nvram/wifiDbDbg
- touch /nvram/wifiWebConfigDbg
- touch /nvram/wifiHalDbg
- touch /nvram/wifiCtrlDbg
- touch /nvram/wifiMonDbg
- touch /nvram/wifiDMCLI
- touch /nvram/wifiLib
- touch /nvram/wifiLibhostapDbg
check for the respective logs in /tmp,
- tail -f wifiCtrl &
- tail -f wifiHal &
- tail -f wifiMgr &
- tail -f wifiDMCLI &
tail -f wifiDb &
- tail -f wifiWebConfig &
- tail -f wifilibhostap &
Wi-Fi 7 segment:
Initial Headers: https://code.rdkcentral.com/r/plugins/gitiles/rdkb/components/opensource/ccsp/halinterface/+/490e08dc0edc9180a18c60eb4d6d3b0c85a1ebe3
Below things will be supported by Onewifi as part of Wi-Fi 7 which includes changes in onewifi ,rdk-wifi-hal & libhostap(for Wi-Fi 7 we use libhostap 2.11 version )
- 320 MHZ
- 4kQAM
- MLO