Introduction
...
Containers offer a logical packaging mechanism in which applications can be abstracted from the environment in which they run. Containers are often compared with virtual machines (VMs). a guest operating system such as Linux or Windows runs on top of a host operating system with virtual access to the underlying hardware. Like virtual machines, containers allow to package your application together with libraries and other dependencies, providing isolated environments for running your software services.
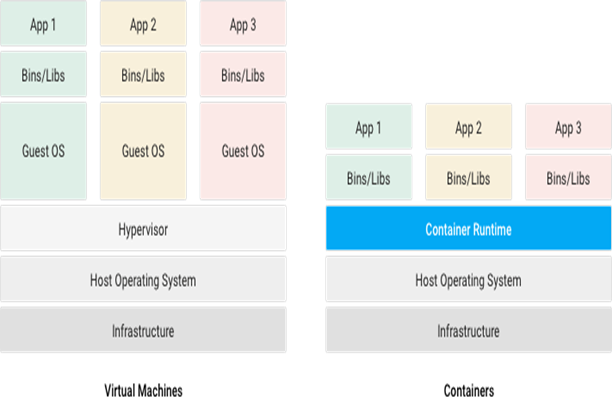 Image Added
Image Added
Why Containers?
- Instead of virtualizing the hardware stack, containers virtualize at the operating system level, with multiple containers running atop the OS kernel directly which means containers are more lightweight: they share the OS kernel, start much faster, and use a fraction of the memory compared to booting an entire OS.
- Container consists of an entire run-time environment: an application, plus all its dependencies, libraries and other binaries, and configuration files needed to run it, bundled into one package. By containerizing the application platform and its dependencies, differences in OS distributions and underlying infrastructure are abstracted away.
Advantages of Containers
- A container may be only tens of megabytes in size, whereas a virtual machine with its own entire operating system may be several gigabytes in size.
- Containerization allows for greater modularity. Rather than run an entire complex application inside a single container, the application can be split in to modules.
Implementation details
...
Summary
The purpose of this section is to describe the new implemented solution to have a secure containerized RDK build on emulator. This implementation done from the reference of
Raspberry pi platform.
The intent of this page is to be used as a walk-through to all the relevant information present in the section.
Detailed organization
The section is organized in two main subsections, as the following:
- Implementation details: here is described all the relevant developments to have containers working.
- Implemented containers: here is detailed information about each container that is already implemented.
- Building procedure.
Most of the information is present in Implementation details, that is organized as the following:
Containers layer - meta-rdk-containers:
- Consists of The main container image(rdk-generic-hybrid-lxc-image) is taken from this layer. Modifications made to this image file so that it
- will be using latest Latest "lxc-container-generator" has been added for container generation at do_rootfs stage.
- Distro feature and latest lxc preferred version also updated in qemux86hybsecurein qemux86hybsecure.conf of this layer.
Emulator
...
layer - meta-rdk-bsp-emulator:
- Added This layer has been used for adding emulator specific package groups and plugins to the container image.
New Container generation process:
This subsection describes how the new container generation process is replacing the earlier process. Main focus in the following topics:
- In this
process - process containers
will - will be generated using "
lxc- lxc-container-generator" recipe, which will use corresponding .xml files to
generate - generate containers.
Here all - All dependencies(such as required binaries,libraries,script files)
will - will be provided in each container .XML file.
- For permissions of
files we also maintain separate - files "add-users-groups-file-owners-and-permissions.inc" file has been added.
While doing rootfs this lxc-container-generator-native component will generate containers in - At rootfs stage containers will be generated in /container path of rootfs.
- Each container will consists of corresponding script (.sh)
file - file for launching that particular container.
Here every - Every process will be launched from corresponding component service file. Single (or) multiple processes can be launched/attached to container.
XML and conf files:
- All required XML and configuration files are placed along with lxc-container-generator recipe in meta-rdk-bsp-emulator layer.
...
Service files:
...
- In platformcontrol container: As we are running three processes we need three
Three service files added for launching
...
corresponding processes inside container
...
Three services are
(sysmgr.service
...
, irmgr.service
...
and dsmgr.service) .
- In rmfstreamer container: As we are launching rmfstreamer process we need
- Note: All these service files are overridden in corresponding receipe .bbappend files based on distro feature "lxc-secure-containers" .
- For exmaple sysmgr.service,irmgr.service and dsmgr.service files are overridden in iarmmgrs_git.bbappend file in meta-rdk-bsp-emulator.
- rmfstreamer.service file overridden in rmfstreamer_git.bbappend in meta-rdk-bsp-emulator.
Implemented containers is updated with all containers that are already implemented. Currently, the following ones are available:
- platformcontrol: runs sysmgr,irmgr and dsmgr processes;
- rmfstreamer: runs rmfstreamer;
- wpelauncher: runs wpelauncher;
Now deprecated. So trying to replace this container with rdkbrowser2.
Building procedure:
rmfstreamer.service file has been added.
- In rdkbrowser2 container:
rdkbrowser2.service file has been added.
Implemented containers
...
Platformcontrol
- runs sysmgr,irmgr and dsmgr processes inside container.
- sysmgr will be launched in new container using lxc-execute.
- irmgr and dsmgr processes has been attached to same container using lxc-attach.
Rmfstreamer
- runs rmfstreamer inside container.
- rmfstreamer will be launched in new container using lxc-execute.
Rdkbrowser2
- runs rdkbrowser2 browser application inside container.
- westeros will be launched in new container using lxc-execute.
- rdkbrowser2 will be attached to the same container using lxc-attach.
Note: As we are in the plan of bringing APPmanager as default application we are not running rdkbrowser2 service file on boot-up.
Building procedure
...
- repo init -u repo init -u https://code.rdkcentral.com/r/manifests -b rdk-next -m rdkv-asp-extsrc.xml
- repo sync --no-tags
- source meta-cmf-bsp-emulator/setup-environment
- meta-rdk-containers/conf/machine/qemux86hybsecure.conf
bitbake rdk- bitbake rdk-generic-hybrid-lxc-image
Container verification
...
- pstree can be used to track the list of containers running as below.
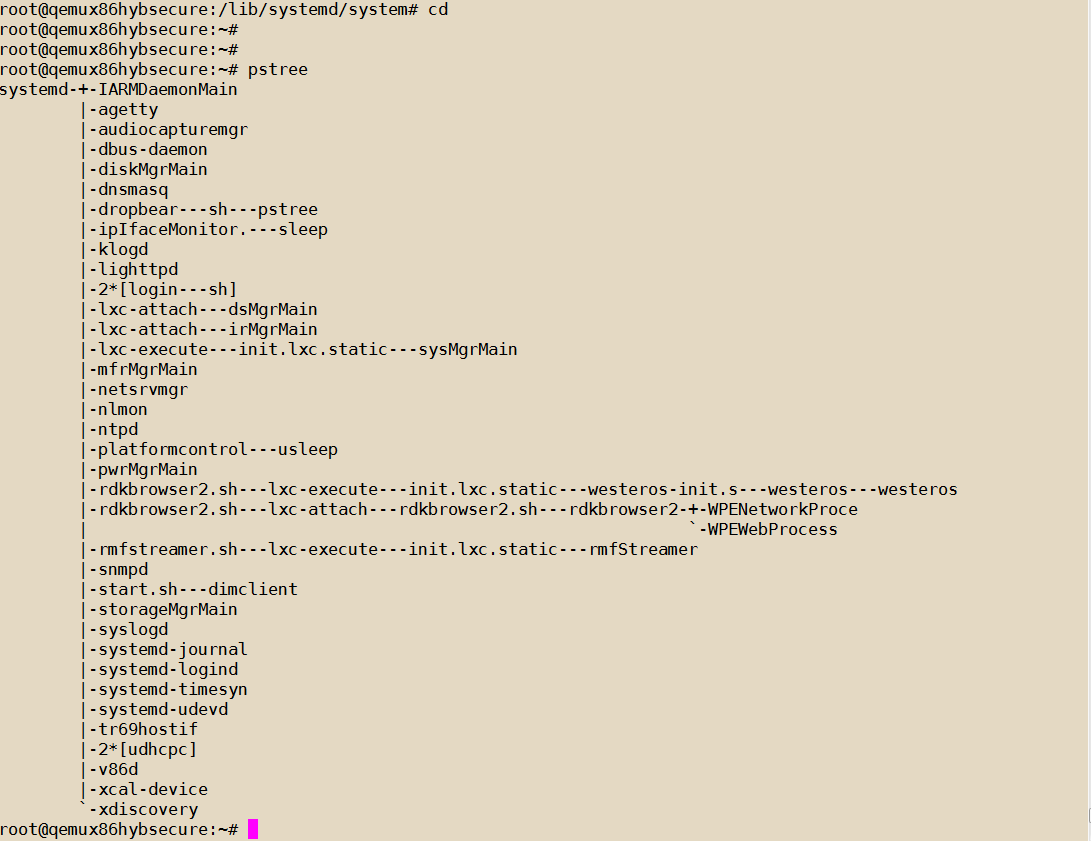 Image Added
Image Added
- ps -Af | grep lxc also lists the current running containers.
 Image Added
Image Added
DEBUG Logs
...
- strace can give more debug information about containers:
Example:
strace -f -o lxc-execute.log /usr/bin/lxc-attach -n PLATFORMCONTROL -f /container/PLATFORMCONTROL/conf/lxc.conf
-u 704 -g 704 -- /usr/bin/dsMgrMain
- lxc-execute.log for debugging purpose.
Test cases
...
- RMFAPP can be used to verify rmfstreamer container.
Example: play http://192.168.2.68:8080/vldms/tuner?ocap_locator=ocap://0x125d - RDKBROWSER2 can be used to launch any URL.
Example: systemctl enable rdkbrowser2.service
systemctl start rdkbrowser2.service - user can see the webpage in rdkbrowser2.
If user wants to change URL, then we need to enter into this container and need to change rdkbrowser2.sh binary as below:
systemctl stop rdkbrowser2.service
systemctl stop westeros-setup.service\
use command:
/usr/bin/lxc-execute -n RDKBROWSER2 -f /container/RDKBROWSER2/conf/lxc.conf – /bin/sh
and then change url in /usr/bin/rdkbrowser2.sh file inside this container environment.
Reference
...
![]()