You are viewing an old version of this page. View the current version.
Compare with Current
View Page History
« Previous
Version 6
Next »
INTRODUCTION
MAC addresses are uniquely assigned to each card, so using MAC filtering on a network permits and denies network access to specific devices through the use of blacklists and white-lists. While the restriction of network access through the use of lists is straightforward, an individual person is not identified by a MAC address, rather a device only, so an authorized person will need to have a white-list entry for each device that he or she would use to access the network.
Mac Filtering mode falls on the following
TR-181 Data Model Parameter of Remote Management
Module | Data Model Params |
Ccsp-Wifiagent | dmcli eRT setv Device.WiFi.AccessPoint.1.X_CISCO_COM_MACFilter.Enable dmcli eRT setv Device.WiFi.AccessPoint.1.X_CISCO_COM_MACFilter.FilterAsBlackList dmcli eRT setv Device.WiFi.AccessPoint.1.X_CISCO_COM_MacFilterTable.1.MACAddress dmcli eRT setv Device.WiFi.AccessPoint.1.X_CISCO_COM_MacFilterTable.1.DeviceName
|
Parameter Work Flow
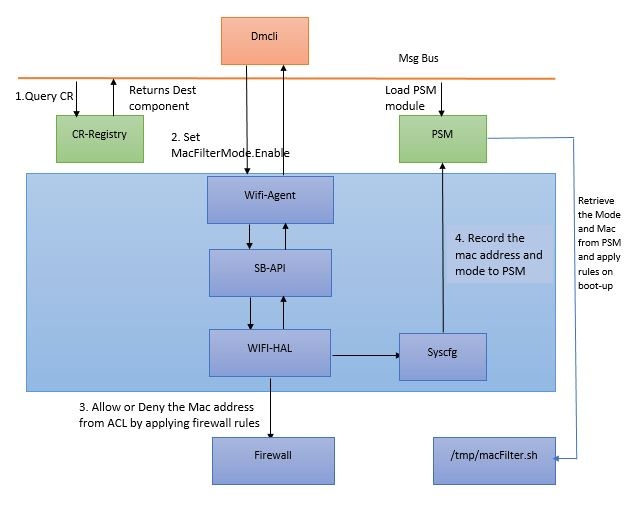
Mac Address are entered via WEBUI or dmcli and stored in ACL(Access Control List) . When the MacFilter mode is set TRUE , it involves either white-list or black-list depends on FilterAsBlackList value, and applying the iptable rules on mac's in ACL. Also record the FilterMode and mac addresses into PSM (Persistent Storage Manager) by syscfg. Retrieves the FilterMode and Mac on boot-up from PSM , rules are applied by executing the macfilter.sh.
Sequence Diagram
1) Adding MAC address into ACL

2) Applying rules on MAC in ACL list
